Ergonomic tips
Resolving common office pain
Strain injuries from repetition, force, and posture are most common for workers with desk jobs. Ergonomic workstations provide the adjustability required for the right fit between our bodies, tools, and tasks—keeping you comfortable and healthy.
Head and neck
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat. Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse cillum dolore.
- Avoid craning forward, keep head in-line with torso
- Check monitor distance from eyes, keep monitor arm distance away
- Adjust/increase text size
Shoulders
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat. Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse cillum dolore.
- Avoid twisting at neck, keep primary monitor straight ahead
- Check work surface height—too high or too low will cause muscle tension
- Check mouse distance (try moving elbow closer to the body)
Lower back
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat. Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse cillum dolore.
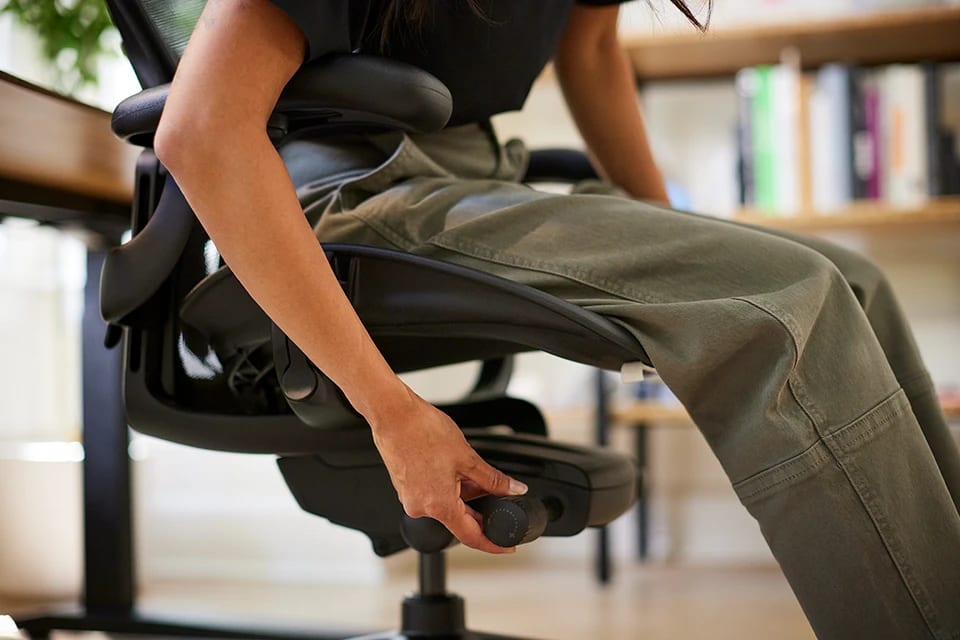
- Check chair height, knees should be approximately 90°, thighs parallel to floor
- Avoid slouching towards monitor
- Check if seat pan depth is preventing use of backrest
Hand numbness
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat. Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse cillum dolore.
- Check wrist angle—arm should be straight from elbow to fingertips
- Avoid twisting at neck, keep primary monitor straight ahead
- Check for high contact pressure on wrist or forearm
Foot and leg numbness
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat. Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse cillum dolore.
- Check seat pan depth, keep two to three fingers’ distance between back of knee and chair
- Check chair height, knees should be approximately 90°, thighs parallel to floor
- Feet supported on floor or footrest
Eye strain
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat. Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse cillum dolore.
- Check monitor distance from eyes, keep monitor an arm's distance away
- Check monitor height, sightline should fall on the top third of the screen
- Every 20 minutes look at something 20 feet away for 20 seconds
- Wear bifocals? Tilt your screen up slightly or lower monitor